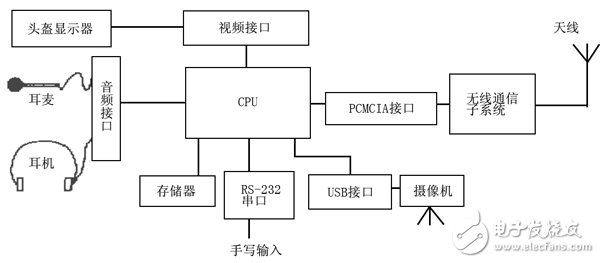
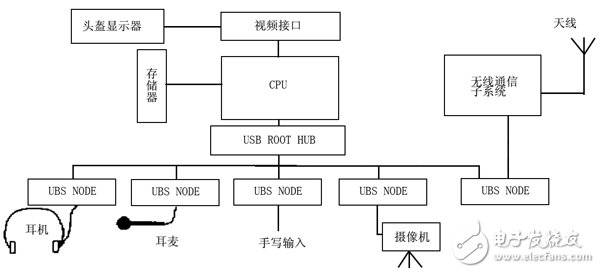
Abstract : Small size, strong function, multiple peripheral devices and high integration are one of the main features of wearable computers. Because wearable computers have high requirements for multimedia, there are many functions to be implemented, so that there are many types of peripherals, so there are many types of interfaces, such as serial port, MCP interface, USB interface, and PCMCIA interface. If these many interfaces are integrated, not only the design is complicated, but also the volume after integration is still large, and its expandability is also low. The USB interface unifies these different interfaces and uses a 4-pin plug as a standard plug. The use of the USB interface as the main peripheral interface in the design of the wearable computer can make up for the above shortcomings. The focus is on wearable computing technology, USB technology and a design method of using USB interface as a universal interface for wearable computers. 1 Introduction At the end of the twentieth century, when network computers began to gradually replace personal computers, a new generation of Wearable Computers came quietly around us. The concept of wearable computing has opened up a new way for the organic combination of human and computer, and is one of the new technologies to achieve more friendly human-computer interaction. Although the wearable computer is small in size, it has all the functions of a PC, such as voice input and output functions, video output functions, image acquisition functions, and wireless communication functions. These functions not only require a variety of different peripheral devices, but also require the peripheral interface to transfer data faster, which undoubtedly increases the difficulty of peripheral interface design, and has become one of the bottlenecks and key technologies in the design of wearable computers. . Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a new interface technology used in the PC field. It has been used by seven world-renowned computer and communication companies such as Intel, Compaq, Digital, IBM, Microsoft, NEC and Northern Telecom for nearly two years. The USB specification officially established in November 1995. USB is a high-speed, half-duplex, isochronous, dynamically connected (hot-swappable), low-cost serial interface that meets the needs of today's and tomorrow's computer platforms. Applying the USB interface to the wearable computer not only can make full use of the universal, high-speed, scalable and hot-swappable features of the USB interface, but also greatly simplify the design of the wearable computer, and improve its integration is to solve the wearable computer. An effective method of interface bottleneck is also a new direction for the development of wearable computing technology. 2 Development of wearable computing technology The concept of "wearable computing technology" was proposed by Edward O.Thop as early as 1955. As with most other mathematical theorems, this concept is also derived from a gambling game. At the time, there was a gambling game called "roulette" that was very popular, and Edward O.Thop wanted to figure out the mystery, but in order to escape the surveillance of the casino, Edward thought that if there was a small computer that he could carry with him. Installed in the pocket, using the small camera device it carries to record the "roulette" rotation process (speed and time), and then use the computer for data processing, you can predict the outcome of the game in advance. For this purpose, Edward and Claude Shannon developed the first wearable computer in 1966. The system is a cigarette box-sized analog computer with four buttons. A data collector uses buttons to capture and display roulette. The speed and pass the result to the gambler through the audio signal to guide him to place a bet. Although the machine function at that time was relatively simple, it represented a new idea and research direction. Since Edward O.Thop proposed the concept of "wearable computing technology", many people have realized its importance and have carried out research, such as Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) and MIT (MIT). Established wearable technology research labs and developed their own wearable computers. Throughout the various wearable computers, it is not difficult to find that the commonality is that human-computer interaction is more convenient, mobile computing, small size, light weight, low power consumption, strong function, and easy to carry, so that the hands are completely controlled from the computer. Freed, so its application is also very extensive. In medical treatment, it can be used for surgery; in the industry, it can help engineers and maintenance personnel to carry out maintenance and maintenance work; in the tourism industry, it can assist navigation; in the military, it can be used to complete military reconnaissance, command decision-making and remote cooperative operations. : In daily life, you can help people remember important things, and so on. The main components of wearable computers include: low-power embedded CPUs, a wide range of portable peripherals, and their interface devices and power supplies with high energy and small size. The basic peripherals mainly include output devices and input devices. In order to facilitate carrying, a helmet display or a glasses display is used instead of the traditional desktop desktop display as an output device, and a conventional keypad is replaced by a voice control or a less-keyed keypad. equipment. In addition, according to the different needs of users, it is also necessary to equip corresponding external devices, such as wireless communication devices, voice input and output devices, image acquisition devices, global positioning systems (GPS) and various sensors. However, in order to integrate these numerous peripherals organically, the corresponding interface circuit must be integrated on the motherboard, so interface circuit design technology is one of the key technologies in wearable technology, in addition to system integration technology, low power Consumption design techniques and augmented reality technologies. 3 USB Technology Introduction USB is an industrial standard expansion bus based on PC. The purpose of developing USB bus specification is: 1 easy to expand PC peripherals; 2 to provide a high transmission rate, low cost solution; 3 support audio, video and Real-time transmission of compressed video data; 4 flexible protocol, can achieve mixed mode of isochronous data transfer (1sochronous Data Transfers) and asynchronous messaging (Asynchronous Messaging); 5 support general commodity equipment; 6 adapt to various computer configuration methods; Provides a standard interface for quick integration into products; 8 is a new class of devices that enhance computer functionality. The main features of USB are: 1 easy to use, easy to install and configure. Installing a USB device eliminates the need to open the chassis, add new devices, or remove installed devices without shutting down the computer. All USB devices support hot swap, the system automatically configures them, completely discarding past jumpers and dip switches. Settings. 2 fast, suitable for a variety of devices with a bandwidth ranging from 1.5Mbps to 12Mbps (USB2.0 supports up to 480Mbps transmission rate), and can support many devices operating at the same time, making full use of the channel bus. 3 Easy to expand, multi-select 127 peripherals can be docked by using the Hub extension. The standard USB cable is 3 meters (5 meters, low speed). Peripheral distances can reach 30 meters via a hub or repeater. 4 can be powered by bus, USB bus provides up to 5V, 500mA current. 5 flexible use, USB has a total of four transmission modes: control transmission, synchronous transmission, interrupt transmission, bulk transmission to meet the needs of different devices. 6 strong and strong. The protocol includes error handling and error recovery mechanisms to automatically identify the wrong device. The composition of the USB system: The USB system is mainly composed of a main controller, a USB hub, and a USB peripheral. The composition of the system topology is shown in Figure 1, at most to 5 layers. 4 USB technology in the wearable computer specific application The following is an example of a wearable computer used to assist a civil aviation aircraft technician to overhaul an aircraft, and specifically describes the application of the USB technology therein. Depending on the actual needs of the aircraft technician, the wearable computer should have peripherals such as a head-mounted display, headphones, headset, camera, wireless communication, and handwriting input. The display is used to display the technical information of the various parts of the aircraft, eliminating the burden of the aircraft technician carrying heavy technical manuals; the earphones and headsets are used for communication between aircraft technicians and technicians and experts at headquarters; the cameras are used to make some troubles The scene is taken into a picture for transmission back to the headquarters; the tablet facilitates the aircraft technician to enter certain maintenance plans into the computer in the form of sketches, and transmits them to the headquarters via wireless communication devices, or inputs some handwriting into the computer for processing. The block diagram is shown in Figure 2. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that there are many computer interfaces, which not only increases the difficulty of system design, but also is not conducive to the integration of the system. At the same time, the power consumption is large, which is not conducive to the realization of the whole system. If the USB interface is replaced by the above interface other than the helmet display interface, the system interface design can be greatly simplified, the integration degree can be improved, the volume can be reduced, and the power consumption of the system can be reduced. The block diagram of the USB interface is shown in Figure 3. The interface type is relatively simple. In addition to the video interface, other peripherals can be connected to the system through the USB interface, so it can be integrated into an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), which simplifies the system structure of the wearable computer. In addition, the USB interface provides three working states of connection, suspend and disconnection, which can effectively save energy and reduce power consumption. USB also supports dynamic plugging and unplugging, automatic identification of devices, which is convenient for users to temporarily assemble peripherals, which improves the flexibility of the whole machine and is also convenient to carry. 5 Conclusion Wearable computing technology is a new technology for the development of next-generation computers. It is currently developing very rapidly abroad, but it started late in China. There are many technologies covered, including voice control technology, voice and image input, compression and decompression technology, wireless communication technology, system integration technology and low-power technology. The application of USB devices has been in a high-speed development stage abroad, and its application in China has already started. Applying USB technology to wearable technology is an effective solution to the development of wearable technology, and will surely receive more attention. Radiators in this case are manufactured with Stainless steel (SS304, SS316 and SS316L). Stainless Steel Radiator,Stainless Steel Transformer Radiator,Stainless Steel Cooling Radiator,Stainless Steel Weather Proof Radiator Shenyang Tiantong Electricity Co., Ltd. , https://www.ttradiator.com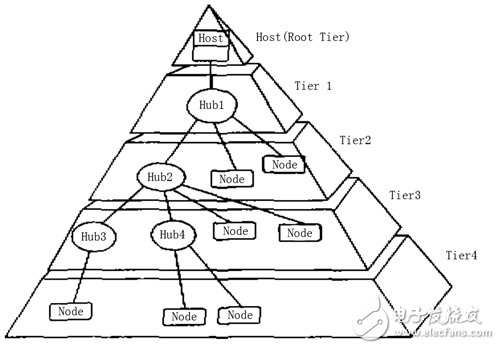
——This article is selected from the electronic enthusiast website February February “Wearable Technology Special Issue†“Perspective New Design†column, please indicate the source, please do it!
These radiators are manufactured with both 1mm CRCA sheet and 1.2 mm CRCA sheet as required and centre distance varying from 600 mm to 4000 mm. Stainless steel radiators can be offered with and without paint.
Through the method, the stainless steel plate type radiator for the transformer is simple in structure, free of complex treatment process on the surface of the radiator, not prone to oxidizing and corroding, long in service life, and high in welding strength.