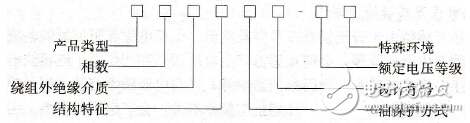
A voltage transformer (PotenTIaltransformer PT, Voltage Transformer, also referred to as VT) is similar to a transformer and is an instrument used to change the voltage on a line. However, the purpose of transforming the voltage of the transformer is to deliver electrical energy, so the capacity is very large, generally in kilovolt-amperes or megavolt-amperes; the purpose of the voltage transformer to convert the voltage is mainly for measuring instruments and relays. The protection device is used to measure the voltage, power and power of the line, or to protect valuable equipment, motors and transformers in the line when the line fails. Therefore, the capacity of the voltage transformer is very small, generally only a few volt-amperes. Dozens of volt-amperes, no more than one thousand volt-amperes. The entry introduces its basic structure, working principle, main types, wiring methods, precautions, anomalies and processing, and ferromagnetic resonance. The basic structure of a voltage transformer is very similar to that of a transformer. It also has two windings, one called primary winding and one called secondary winding. Both windings are mounted or wound around the core. There is insulation between the two windings and between the windings and the core, so that there is electrical isolation between the two windings and between the windings and the core. When the voltage transformer is running, the primary winding N1 is connected to the line, and the secondary winding N2 is connected to the meter or the relay. Therefore, when measuring the voltage on the high-voltage line, although the primary voltage is high, the secondary is low-voltage, which ensures the safety of the operator and the instrument. The working principle is the same as that of the transformer, and the basic structure is also the core and the primary and secondary windings. The characteristic is that the capacity is small and relatively constant, and it is close to the no-load state during normal operation. The impedance of the voltage transformer itself is very small. Once the secondary side is short-circuited, the current will increase sharply and the coil will be burnt. For this reason, the primary side of the voltage transformer is connected with a fuse, and the secondary side is reliably grounded to prevent the primary side and the secondary side from being damaged, and the secondary side has a high potential to the ground, causing personal and equipment accidents. The measuring voltage transformers are generally made into a single-phase double-coil structure, and the primary side voltage is the measured voltage (such as the line voltage of the power system), which can be used in single phase, or two sets can be used to form a three-phase VV. use. Laboratory voltage transformers are often multi-tap on the primary side to accommodate the need to measure different voltages. The voltage transformer for protection grounding also has a third coil, called a three-coil voltage transformer. The third coil of the three phases is connected to an open triangle, and the two terminals of the open triangle are coupled to the voltage coil of the ground protection relay. In normal operation, the three-phase voltage of the power system is symmetrical, and the sum of the three-phase induced electromotive forces on the third coil is zero. When a single-phase grounding occurs, the neutral point is displaced, and a zero-sequence voltage appears between the terminals of the open triangle to cause the relay to operate, thereby protecting the power system. When the coil has zero-sequence voltage, the zero-sequence flux will appear in the corresponding core. To this end, the three-phase voltage transformer uses a side yoke core (10KV or less) or three single-phase voltage transformers. For this kind of transformer, the accuracy of the third coil is not high, but it requires a certain overexcitation characteristic (that is, when the primary side voltage increases, the magnetic flux density in the core also increases by a corresponding multiple without damage). Voltage transformers are indispensable for power transmission and power supply systems such as power plants and substations. Precision voltage transformers are instruments used in electrical test laboratories to expand the limits and measure voltage, power and electrical energy. Voltage transformers are very similar to transformers and are used to change the voltage on the line. Why do you need to change the voltage on the line? This is because, depending on the power generation, transmission and power consumption, the voltage on the line varies, and the difference is very different. Some are low voltage 220V and 380V, and some are high voltage tens of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of volts. To directly measure these low voltage and high voltage voltages, it is necessary to make corresponding low voltage and high voltage voltmeters and other instruments and relays according to the line voltage. This will not only bring great difficulties to the instrument production, but more importantly, it is impossible to directly produce high-voltage instruments and measure the voltage directly on the high-voltage line, and it is absolutely not allowed. The model of the voltage transformer is expressed in Chinese Pinyin letters and is composed as follows: (1) Product category, the symbol is J, indicating the voltage transformer. (2) Phase number, S-three phase; D-single phase. (3) The outer insulating medium of the winding is indicated by the following letters: G-dry; Q-gas insulation; Z-cast insulation; oil immersion is not indicated. (4) Structural features, indicated by the following letters: X-band zero-sequence voltage winding; B-three-column with compensation winding; W-five-column three-winding; C-Cascade with zero sequence voltage winding; F-Measure and protect separate secondary windings. (5) Oil protection mode, N-without metal expander; with metal expander not shown. (6) Serial number, expressed in numbers. (7) Rated voltage in kV. (8) Special circumstances, indicated by the following letters: GY-plateau area; W-soil area; TA-dry area; TH-tide area. For example, the JDX-110 model represents a single-phase, oil-immersed, 110kV voltage transformer with zero-sequence voltage windings.
With more than 15+ yrs rich MFG experience, you can definitely trust in and cooperate with.
protective equipment, ppe personal protective equipment, definition of personal protective equipment TOPNOTCH INTERNATIONAL GROUP LIMITED , https://www.itopnoobluetoothes.com
Provide you with the supply of personal protective equipment. to help you safely get back to your daily routine.
Our products include pulse Oximeter Finger, Forehead Thermometer, Automatic foam soap dispenser, etc.
Our strict quality control protocol thoroughly vets every aspect of production, storage, and shipments all the way way to our end customers.
What is a voltage transformer?