In response to the global financial turmoil, the Central Development and Reform Commission has allocated 4 trillion yuan together with local financial support. It is estimated that more than 10 trillion yuan will be invested in national transportation, supporting enterprises, and improving infrastructure. Recently, the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China launched the "Ten Cities and Ten Thousand Miles" LED street lighting semiconductor lighting application project in the country. Under this strong east wind, the semiconductor lighting industry, which has consistently received government support, will be an opportunity for great development. Many companies are optimistic about the development of this sunrise industry, especially the obvious energy-saving advantages of semiconductor outdoor lighting. In the past two years, many companies that have been rushing to the top, under the characteristics of semiconductor road lighting production, have simulated, counterfeit, and made a variety of "snake heads" in the shape of today's conventional lighting street lamps. At one time, "a hundred schools of thought contend, flowers bloom." The products have been introduced to the market. After two years of testing on the road, most of the products have different degrees of problems.
Specifically in:
1. Due to the lack of understanding of the working conditions of the LED light source, the light attenuation is severe or even dead.
2. Insufficient perception of road lighting requirements, scientific point light source optical light distribution difficulties and neglect of the importance of color temperature in road lighting, easy to cause glare, zebra effect and in the environment of serious air pollution, rain and foggy weather, The phenomenon that the light is not bright enough on the ground.
3. Insufficient understanding of the LED operating conditions and the technicality of the power supply, resulting in endless product failures on the power supply.
4. The application concept of the practical road of LED street lamps is unclear. Blind and high-power gas discharge lamps are “comparable†to produce super-power LED street lamps without cost, which makes it difficult to promote unrealistic and expensive street lamp products.
5. The requirements for road lighting are vague, and the actual use and maintenance are not considered, resulting in the direct use of the owner's boycott.
I will discuss the solution with you on the above issues:
The discussion of the working environment of the LED light source needs to have the basic knowledge of understanding the LED; the core of the LED is the PN junction. Therefore, it has the IN characteristic of a general PN junction, that is, forward conduction, reverse cutoff, and breakdown characteristics. In addition, it has luminescent properties under certain conditions. At the forward voltage, electrons are injected into the P region from the N region, and holes are injected into the N region from the P region. A part of the minority carriers (small children) entering the other area is combined with the majority carriers (multi-sub) to emit light. The current high-power LED luminous efficiency is about 30%, and 70% will be heat energy, which needs to be heat-dissipated. As shown in Figure 1. (Figure 1)
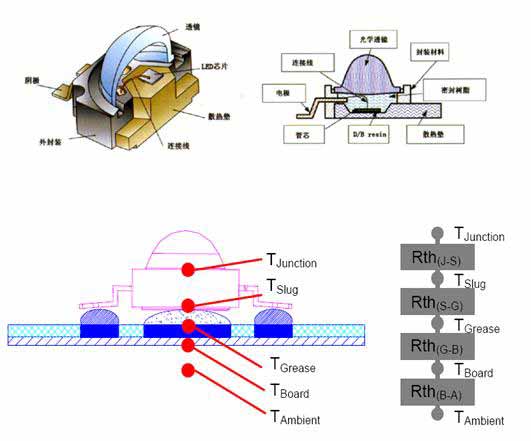
Table 2 shows the relationship between the junction temperature TJ of high-power white LEDs and the lifetime when the brightness is attenuated by 70% (the life of different LED manufacturers is not the same, only for reference).
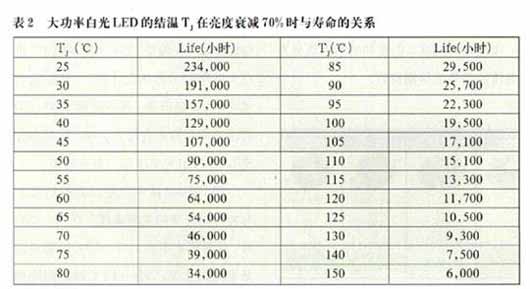
It can be seen in Table 2 that when TJ=50°C, the life is 90,000 hours, when TJ=80°C, the life is reduced to 34,000 hours, and when TJ=115°C, the life is only 13,300 hours. TJ should propose the maximum allowable junction temperature value TJmax in the heat dissipation design. The actual junction temperature value TJ should be less than or equal to the required TJmax, ie TJ≤TJmax.
From the above test data, the ambient temperature at which the tested LEDs can work properly should be (<85 °C). Above this temperature range, the efficiency will be greatly reduced, even burning. As shown in table 2.