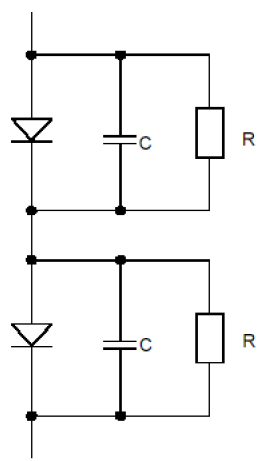
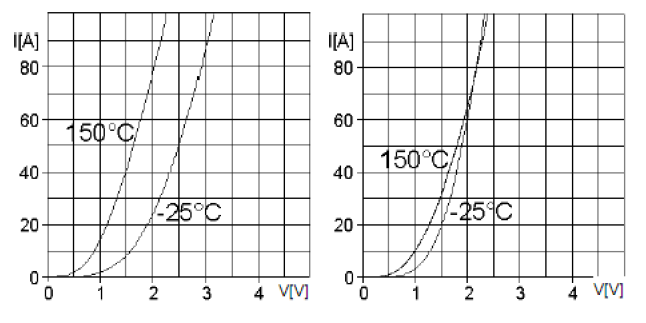
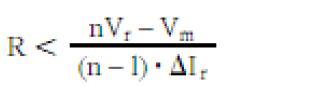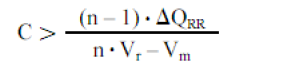Diode in series Diode devices must be aware of their static and dynamic voltage equalization when used in series. Figure 1 Series application of the device The device is used in series. In static mode, the leakage current of each component in series is inconsistent, so that the component with the smallest leakage current is subjected to the highest voltage and even reaches its rated limit value, so it must be connected in parallel. For a series circuit of n diodes, we can get a simplified formula for calculating the resistance: In the above formula: the number of n-series components; the rated voltage of the Vr-diode; the maximum value of the voltage in the Vm-series circuit; ΔIr-the leakage current deviation value of the diode operating at the highest operating temperature. Experience has shown that the solution to the dynamic equalization problem is always different from the static equalization problem. If the carrier of a diode pn junction disappears faster than the other, it also withstands the voltage earlier during the turn-off process. When n diodes with a given voltage value of Vr are connected in series, we can calculate the capacitance using a simplified formula: ΔQRR - The maximum deviation of the reverse recovery charge between series elements. When the device used is from the same manufacturing lot number, we can assume △QRR=0.3 QRR. When the device is used in series, the rated parameters of each device in series can be maximized only when the static dynamics of each device reach a fairly ideal symmetric equilibrium state. Usually in the parallel application of power devices, we should first consider current sharing. In the absence of special current sharing measures, the deviation of the on-state voltage of the devices connected in parallel should be as small as possible. The dependence of the on-state voltage on the temperature of the device is an important parameter to measure the parallel application of the device. Some types of devices have a positive temperature coefficient of on-state voltage, and some devices have a negative temperature coefficient. When a device has a positive temperature coefficient, it is more suitable for parallel applications. However, because diodes always have a certain manufacturing variation, a large negative temperature coefficient (>2mV/K) in the parallel application of the diode may make the operating temperature unbalanced. In turn, the device is permanently disabled. Figure 2 Temperature dependence of different types of diodes big horsepower centrifugal switches Motor Accessories Main Board,Electric Centrifugal Motor Start Switches,Electric Motor Centrifugal Switches Parts,Motor Switch For Single Phase Motor Ningbo Zhenhai Rongda Electrical Appliance Co., Ltd. , https://www.centrifugalswitch.com