(*This article is a project funded by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (the solar light importer provides key technologies for architectural optics in Beijing underground space lighting, subject number 8083028) )
[Abstract] Based on the physical core type, cavity prism type and cavity mirror type three kinds of light guide transmission methods, the paper summarizes the system performance and application analysis of the active active tube type natural light introduction system.
[Key words] active natural light introduction system; solid core type; cavity prism type; cavity specular reflection type
Application Research Overview on Active Tubular Daylight Guidance System Based on Light Transmission Technology
YUAN ZONGNAN ZHANGXIN ZHAN QINGXUAN
ABSTRACT: Based on three kinds of light transmission technology, they are solid core systems, hollow prismatic light guides and hollow mirrored guides respectively. Dissertation summarizes system's performances and application analyses of active tubular daylight guidance system that is now a fully-fledged technology.
KEYWORDS: Active Daylight Guidance System; Solid Core Systems; Hollow Prismatic Light Guides; Hollow Mirrored Guides
According to the concentrating method, the tubular natural light introduction system is divided into active type and passive type. At present, in domestic and foreign applications and research, active light collection is the main direction. This paper mainly discusses the application of active light collection types.
A typical tubular natural light introduction system consists of a three-part technology, including an external concentrator, a light guide transmission device, and an internal illuminator. The key technical components are optical transmission devices connected inside and outside, so-called light pipes. According to the existing technical research and practice accumulation, the optical transmission method and technology can be divided into four categories, namely, beam/lens systems, hollow mirrored guides, and hollow prisms. Prismatic light guides), solid core systems [1]. In practical applications, active light collection combined with solid core, cavity prism and cavity mirror transmission forms several mature integrated systems, including the Japanese “Himawari†system transmitted by fiber. HSL (Hybrid Solar Lighting) system in the United States, Solux system in Germany; European Arthelio system with cavity prism transmission; Swiss Heliobus system with mirror mirror transmission, Heliostats system in Berlin and Malaysia.
1 Active system for physical core transmission
1.1 "Himawari" system
The system was developed and developed by Professor Kei Mori in the 1970s, and its first generation appeared in 1979. The light collecting part of the whole system adopts GPS positioning, convex lens group focusing to enhance sunlight illumination, fiber introduction, and automatic sunlight tracking system [2]. The concentrator is composed of a set of hexagonal Fresnel lenses arranged in a honeycomb shape (Fig. 1). The photosensitive device is placed in the center of the concentrator and has an internal clock and a set of microprocessors for tracking the sun. When the weather is good, the solar sensor can accurately determine the position of the sun; when the sun is blocked by the clouds, the concentrator will rely on the calculation of the internal clock and the microprocessor to adjust the direction, so that the cloud movement leaves, no longer When blocking sunlight, the concentrator can accurately locate the sun; when sunset, the system automatically turns to the direction of the sunrise and shuts down the system to the next sunrise based on the clock and processor calculations. [2]
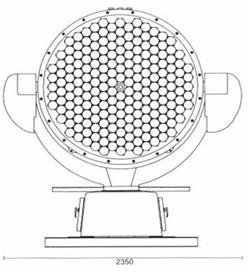
Figure 1 The largest concentrator in the Himawari system. [2]
Each Fresnel lens on the system concentrator is introduced into a 1 mm diameter fiber by focusing sunlight. Several fibers are bundled to form the light guiding transmission portion of the entire system. The smallest composition consists of six Fresnel lenses combined with six fibers, on the basis of which 12, 18 and other combinations are formed. In addition, the incident end of the optical fiber is precisely positioned on the visible light focus between the purple and infrared rays, and the ultraviolet light is largely intercepted by the physical distance difference positioning, and only 1/2160 of the ultraviolet light is tested to enter the room. At the same time, all radioactive rays such as X, Y, Φ, β, γ, and α in the sun are also excluded [2], and finally a small amount of ultraviolet rays, infrared rays, and a large amount of visible light are entered.
The system application data record shows that when the concentrator receives 98000 lx of solar light, each fiber of about 15 meters can output a luminous flux of 1920 lm under the collection of the lens. The ratio of the diameter of the illumination to the sunlight introduced by "Sunflower" is 1.1:1 [2].
The Himawari system has a strong applicability to spaces that emphasize spectral and thermal control, such as aquariums, photosynthetic cell culture chambers. The standard models of the system are “6 mirrorsâ€, “12 mirrors†and “36 mirrorsâ€. The order products are “90 mirrors†and “198 mirrorsâ€. For operation and maintenance, the Himawari system is relatively simple to maintain and has low operating costs. For example, 12 eyes of "sunflower" use about 11 degrees a year, and the transparent dome of the collection unit can be washed with water [2].