How to use DS1678 real-time event recording-How to Use th
DS1678 Pin Assignment
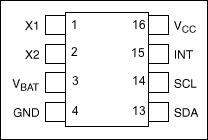
DescriptionThis application note demonstrates how to use the DS1678 real-time event recorder which logs events—level transitions on the INT input pin—into a 1024-word datalog memory array. The first event is recorded as a time stamp; subsequent events are recorded as elapsed time from the previous event. The time stamp and 1024-word datalog memory accommodate up to 1025 recorded events.
This example code includes functions for initiating a datalogging "mission." The user-selectable options are event resolution, trigger selection, and rollover (handling missions of more than 1025 events). The software also includes routines for ending a mission, for displaying the event datalog information, and for writing and reading the user RAM.
OperationThe program uses two general-purpose port pins (GPIOs) on a microcontroller to communicate with the DS1678 through the DS1678's I²C serial interface. An additional port pin is used to toggle the DS1678's INT input to drive events. In a typical application, the INT input would be connected to circuitry that conditions the signals from the event source, eg, a thermostat in a HVAC system. This connection allows the DS1678 to record, for example, the start time and duration of each cooling or heating cycle.
This example uses an 8051-compatible microcontroller, the DS2250. User inputs and data outputs from the program are passed through an RS-232 interface from a terminal emulator program on a PC to a UART on the microcontroller. The Microcontroller Tool Kit software utility can be used to program the DS2250 microcontroller.
The software is shown in Figure 1. A schematic of the circuit is shown in Figure 2.

Download
Figure 1. Program listing for interfacing a microcontroller to the DS1678.
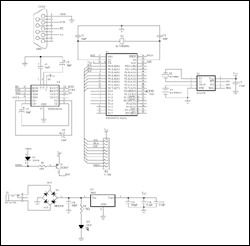
For Larger Image
Figure 2. Schematic for the DS1678 demonstration board.
Semiconductor Fuse and Ferrite
Fuse refers to an electric appliance that, when the current exceeds the specified value, melts the fuse and disconnects the circuit with the heat generated by itself.When the current exceeds the specified value for a period of time, the fuse melts and disconnects the circuit with the heat generated by the fuse itself.A current protector made from this principle.The fuse is widely used in high and low voltage power distribution system and control system as well as power equipment.
Ferrite is a metal oxide with ferrous magnetism.As far as electrical properties are concerned, the resistivity of ferrite is much larger than that of single metal or alloy magnetic materials, and it has higher dielectric properties.Ferrite magnetic energy also shows high permeability at high frequencies.As a result, ferrite has become a non-metallic magnetic material widely used in the field of high frequency and weak current.Due to the low ferrite magnetic energy stored in the unit volume, saturated magnetic induction strength (Bs) and low (usually only pure iron 1/3 ~ 1/5), and thus limits its higher requirements in the low-frequency magnetic energy density in the field of high voltage and high power applications.
Semiconductor Fuse, Fuse Cutout, Protection Fuse, Square Fuse, Fuse Link, Ceramic Fuse, Fuse Box, Fuse Resistors
YANGZHOU POSITIONING TECH CO., LTD , https://www.yzpstcc.com