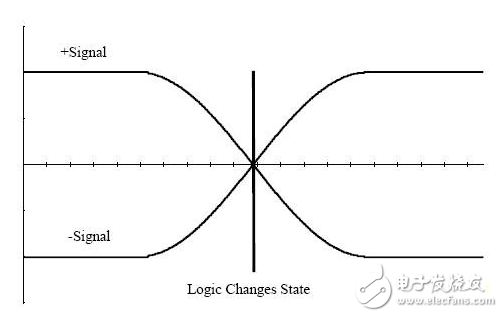
This article details the difference between single-ended and differential signals. Differential transmission is a signal transmission technology. It is different from the traditional one signal line and one ground line. Differential transmission transmits signals on these two lines. The amplitudes of the two signals are equal and the phases are 180 degrees out of phase. The opposite polarity. The signals transmitted on these two lines are differential signals. The first benefit of the differential signal is that because you are controlling the 'reference' voltage, you can easily identify small signals. In a ground-based, single-ended signaling scheme, the exact value of the measured signal depends on the consistency of the 'ground' within the system. The further the source and signal receiver are, the more likely they are to differ between the local voltage values. The value of the signal recovered from the differential signal is largely independent of the exact value of 'ground', but within a certain range. The second major benefit of the differential signal is that it is highly immune to external electromagnetic interference (EMI). An interference source affects each end of the differential signal pair to the same extent. Since the voltage difference determines the signal value, this will ignore any similar interference that occurs on both conductors. In addition to being less sensitive to interference, differential signals generate less EMI than single-ended signals. A third benefit of differential signaling is the ability to accurately handle 'bipolar' signals in a single-supply system. In order to handle the single-ended, single-supply system bipolar signal, we must establish a virtual ground at any arbitrary voltage (usually the midpoint) between the ground and the mains. The positive signal is represented by a voltage higher than the virtual ground, and the negative signal is represented by a voltage lower than the virtual ground. Next, the virtual ground must be correctly distributed throughout the system. For differential signals, such a virtual ground is not needed, which allows us to process and propagate the bipolar signal with a high degree of truth without relying on the stability of the virtual ground. Differential signal waveform and single-ended equivalent The main drawback of the differential circuit is the increase in traces. Therefore, if none of these advantages in your application are particularly important, then it is not worth considering additional areas for differential signaling and accompanying cabling. But if these advantages create significant performance differences in your circuit, then the increased cabling area is the price we pay. A single-ended signal refers to a signal transmitted by one line. How can a signal be signaled without a reference point? The reference point is the ground. That is, the single-ended signal is the level difference between ground and ground transmitted on a wire. Then when you pass the signal from point A to point B, there is a premise that the ground potentials of points A and B should be about the same. A differential signal refers to a signal transmitted by two wires that transmits the level difference between the two signals. When you pass the signal from point A to point B, the ground potentials of points A and B can be the same or different, but the ground potential difference between point A and point B has a range. If it exceeds this range, it will be a problem. . The advantage of single-ended signals is that it saves money and is convenient. Most of the low frequency level signals are transmitted using single-ended signals. One signal is a line. Finally, the two sides of the ground are connected by a single line. The shortcomings are different in different application areas. To sum up, the most important aspect is that the anti-interference ability is poor. First of all, the biggest problem, the ground potential difference and the ground consistency. Everyone thinks that the ground is 0V. In fact, the real application is a strange and unpredictable thing. I think I will write some interesting things about the ground. For example, between point A and point B, there is a line that connects the ground between the two systems. If the current on this line is large, the ground potential between the two points may not be neglected. Such a signal, which looks like 1V from the perspective of A, may seem to be only 0.8V from the perspective of B. This is not a good thing. This is the effect of the ground potential difference on the single-ended signal. Then talk about consistency. In fact, many times this time the current is too large and small on the ground, the layout structure is far and near, and there will be certain voltage fluctuations on the ground, which will also affect the quality of the single-ended signal. The differential signal has an advantage at this point. Since both signals are relative to ground, when the local potential changes, the two signals float up and down at the same time (of course, ideally), and the voltage difference between the two differential lines is very high. Less change, so the signal quality is not high soon? The second is the interference during transmission. When a wire passes through a coil and the coil is connected to alternating current, an induced electromotive force is generated on the wire. In fact, most of the industrial sites encountered. The problem is that simple, but you can't resist it. If it's a single-ended signal, how much is produced, that's how much, that's the noise you have no way. But if it is a differential signal, you can consider pulling it. Why is the two wires transmitted in parallel? Is the induced electromotive force generated on each wire the same? If the two are reduced, he will not be there soon. Indeed, in the same situation, when the transmission distance is long, the differential signal has stronger driving capability and stronger anti-interference ability. Similarly, when the signal you transmit will interfere with other devices, the differential signal is also simpler than the single signal. The signal generated by the terminal signal is relatively small, which is also known as the EMI characteristic.
12V Adapter also called 12V AC DC adapter, the input of 12V power adapter is 100v-240v 50/60HZ suit for worldwide use.
All
our 12v ac adapter with over current protection, over load protection, short
circuit protection, over heat protection.when use it can safeguard your
equipment.
Usually our dc Cable and ac cable compatible with the 12v power adapter is 1.2m, we can also customized the length as your requests according to your devices.
if the adapter you need is not 12V, pls contact us freely, we can also customized the adapter output can your demands. OEM&ODM orders are highly welcomed!
12V Adapter,12V DC Adapter,12V Power Adapter,12V DC Power Adapter Shenzhen Yidashun Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ydsadapter.com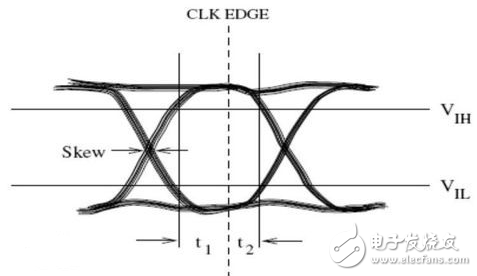

Yidashun can produce 12v power supply from 12V 1A~12V 16A MAX. This power adapter mostly make as dc size 5.5*2.1mm, 5.5*2.5mm, round 4 pin used for led lights, CCTV camera, LCD TV, set-top box and so on. All our adapter with full power and can be used for different devices run constantly each day.


